AWS vs Azure Machine Learning
- Thiru T
- Oct 18, 2024
- 2 min read
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have emerged as dominant players, particularly in the realm of Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS). Both platforms offer tools that enable users to develop and deploy machine learning models with minimal data science expertise, thus democratizing access to advanced analytics (Siddiqui, 2021). This accessibility is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage data-driven insights across various industries, with applications ranging from predicting flight delays to assessing credit risks.
When comparing the machine learning offerings of AWS and Azure, distinct differences in their approaches emerge. Azure typically provides a more integrated suite of frameworks and APIs, facilitating seamless development within existing Microsoft ecosystems (Unknown Author, 2024). In contrast, AWS excels in its compatibility with open-source technologies, granting users greater flexibility in tool selection. These differences highlight how each platform caters to varying organizational needs and technical backgrounds.
Ultimately, the choice between AWS and Azure for machine learning projects depends on specific requirements, such as ease of integration, scalability, and available resources. Organizations are encouraged to carefully assess their unique circumstances before selecting a platform that aligns with their strategic goals (Siddiqui, 2021). By effectively leveraging the strengths of either AWS or Azure, businesses can harness the power of machine learning to drive innovation.
AI vs. ML: Understanding the Difference
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The broader field focused on simulating human thought and decision-making.
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that allows computers to learn from data without explicit programming, as defined by Arthur Samuel.
Core Ingredients for Machine Learning
Data: Large amounts of quality data.
Computation: Algorithms to process data.
Expertise: Knowledge of machine learning principles.
Cloud Computing and Accessibility
Cloud computing has democratized access to ML tools, allowing organizations of all sizes to leverage advanced analytics without the need for extensive expertise or expensive infrastructure.
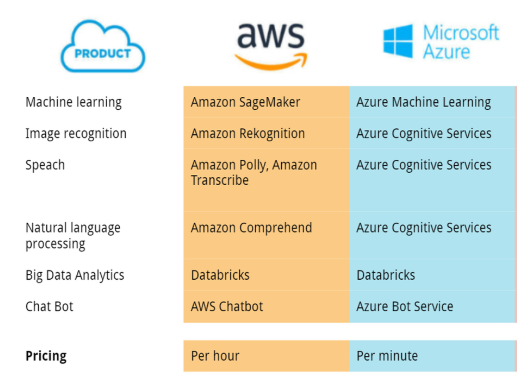
Comparing AWS and Azure in Machine Learning
1. Machine Learning Building Blocks
Speech Services:
AWS: Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Polly
Azure: Speech to Text, Text to Speech
Chatbots:
AWS: Amazon Lex
Azure: Language Understanding
Translation:
AWS: Amazon Translate
Azure: Translator
Text Analytics:
AWS: Amazon Comprehend
Azure: Text Analytics
Document Analysis:
AWS: Amazon Textract
Azure: Form Recognizer
Image and Video Analysis:
AWS: Rekognition
Azure: Computer Vision
Anomaly Detection:
AWS: Amazon Lookout
Azure: Anomaly Detector
Personalization:
AWS: Amazon Personalize
Azure: Personalizer
2. Machine Learning Platforms
Notebooks: All providers offer Jupyter Notebooks.
Framework Support: TensorFlow, MXNet, Keras, etc.
Guided Development:
AWS: SageMaker Autopilot
Azure: Automated ML
Full ML Workbench:
AWS: SageMaker Studio
Azure: Machine Learning Notebooks
3. Machine Learning Infrastructure
Container Support: All providers favor containers for deployment.
Hardware Options:
AWS: Custom ASICs (Trainium, Inferentia)
Azure: FPGA-based VMs
GCP: Tensor Processing Units (TPUs)
Explainability and Bias Management
Each cloud provider offers tools for explainability and bias assessment:
AWS: SageMaker Clarify
Azure: Responsible ML, Fairlearn SDK
GCP: AI Explanations
Conclusion
Choosing between AWS and Azure for machine learning projects depends on specific organizational needs, such as integration ease, scalability, and available resources. By assessing their unique circumstances, businesses can effectively leverage machine learning to drive innovation and achieve strategic goals.


Comments